Geography of India For RPSC RAS Prelims: Power Resources-Conventional & Non-Conventional. Conventional Sources of Energy, also known as non-renewable sources, are those that exist in limited quantities. They include resources like coal and oil, which are not replenished once extracted. They are classified into commercial and non-commercial energy sources. Non-conventional sources are also known as renewable sources of energy. These include solar energy, wind energy, bioenergy, and tidal energy.
Geography of India For RPSC RAS Prelims
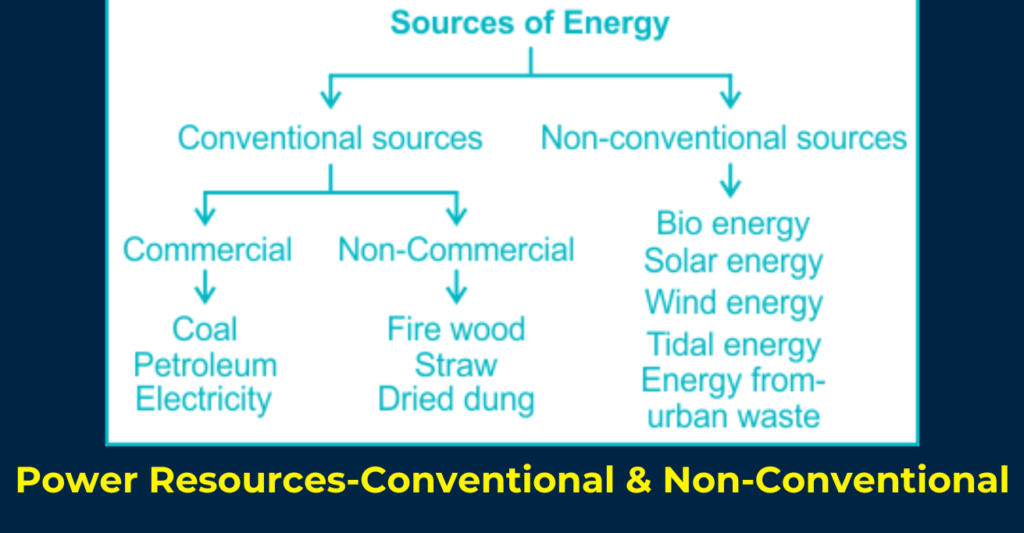
Power Resources-Conventional & Non-Conventional
The two main classifications of energy sources are:
- Conventional Sources
- Non-Conventional Sources
Conventional Sources of Energy
Conventional Sources of Energy, also known as non-renewable sources, are those that exist in limited quantities. They include resources like coal and oil, which are not replenished once extracted.
They are classified into;
- Commercial and
- Non-commercial energy sources
Commercial Energy Sources: Coal, electricity, and petroleum are examples of commercial energy sources. These are resources that consumers must purchase for use.
Non-commercial Energy: Sources Non-commercial energy sources are those that are freely available and do not require purchase. Firewood, animal waste, and straw are examples of such resources.
Non-Conventional Sources of Energy
Non-conventional sources are also known as renewable sources of energy. These include solar energy, wind energy, bioenergy, and tidal energy.
Solar Energy: Solar Energy is derived from the sun. Photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electricity, which can be used for various purposes, including cooking and water purification.
Wind Energy: Wind energy is generated by harnessing the kinetic energy of the wind. It is commonly used to power water pumps for irrigation. India is one of the leading countries in wind power generation.
Tidal Energy: Tidal energy is generated by harnessing the energy of sea tides. While this source of energy has significant potential, its use is limited due to the lack of cost-effective technology.
Also, read:
